
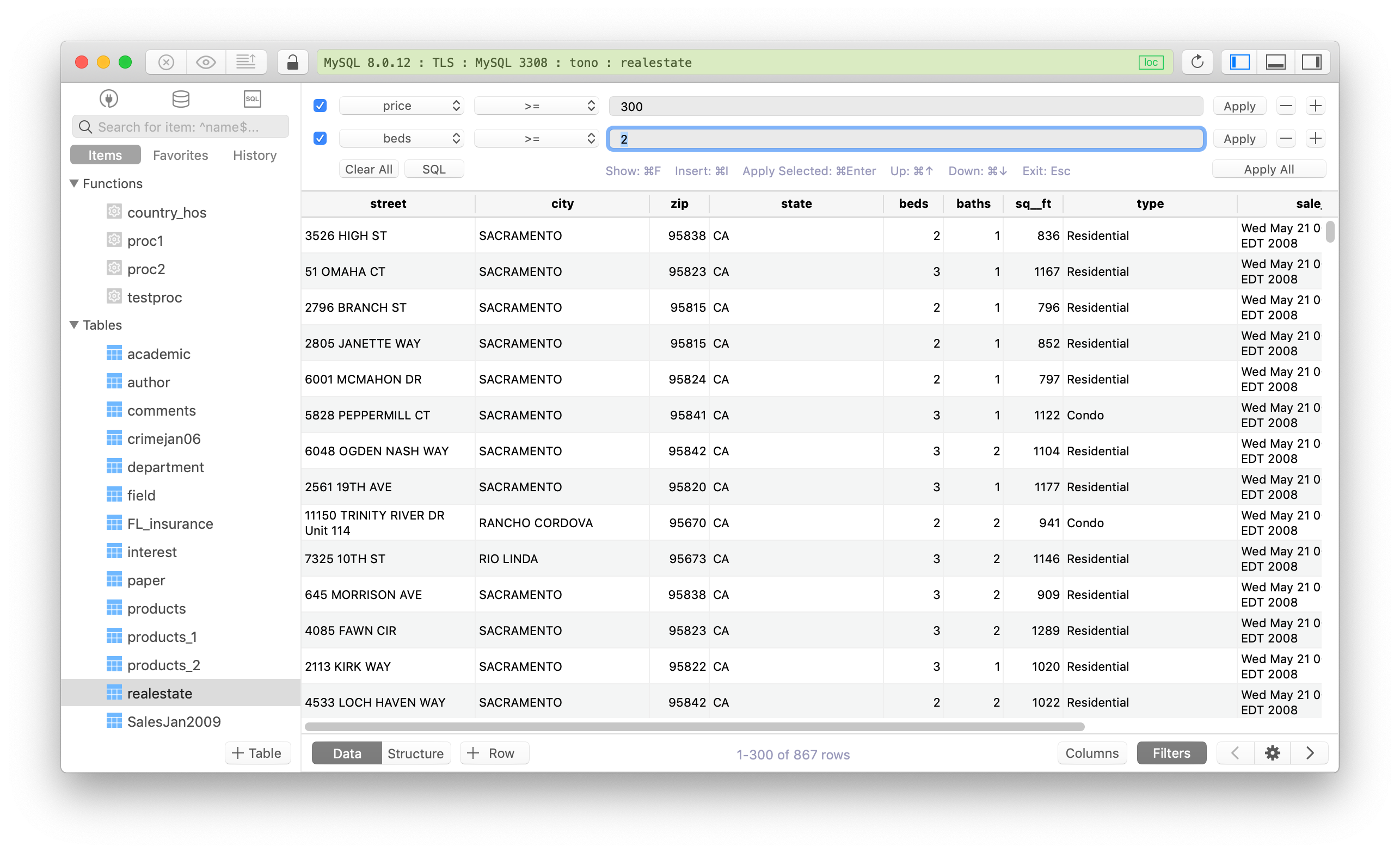
- TABLEPLUS RUN STORED FUNCTION MYSQL HOW TO
- TABLEPLUS RUN STORED FUNCTION MYSQL INSTALL
- TABLEPLUS RUN STORED FUNCTION MYSQL UPDATE
This will mean that you can once again connect to MySQL as your root user using the sudo mysql command. ALTER USER 'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH auth_socket.Then go back to using the default authentication method using this command: To authenticate as the root MySQL user using a password, run this command: Once the security script completes, you can then reopen MySQL and change the root user’s authentication method back to the default, auth_socket.
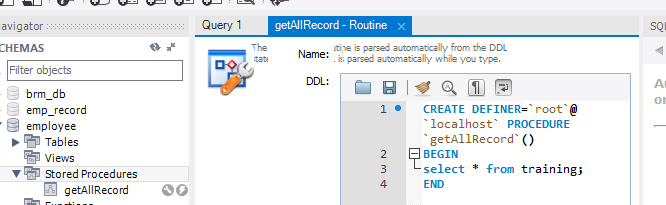
TABLEPLUS RUN STORED FUNCTION MYSQL INSTALL
These commands will install and start MySQL, but will not prompt you to set a password or make any other configuration changes.
TABLEPLUS RUN STORED FUNCTION MYSQL UPDATE
To install it, update the package index on your server if you’ve not done so recently:Įnsure that the server is running using the systemctl start command: At the time of this writing, the version of MySQL available in the default Ubuntu repository is version 8.0.28. On Ubuntu 22.04, you can install MySQL using the APT package repository. To set this up, follow our initial server setup guide for Ubuntu 22.04.

By completing it, you will have a working relational database that you can use to build your next website or application.
TABLEPLUS RUN STORED FUNCTION MYSQL HOW TO
This tutorial will go over how to install MySQL version 8.0 on an Ubuntu 22.04 server. It implements the relational model and uses Structured Query Language (better known as SQL) to manage its data. MySQL is an open-source database management system, commonly installed as part of the popular LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP/Python/Perl) stack.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
